How Two Committed Conservationists Revitalized a River With Beer
Worried about low flow in Arizona’s Verde River, conservationists have found a solution in new crops and a new brew.
How Two Committed Conservationists Revitalized a River With Beer
Worried about low flow in Arizona’s Verde River, conservationists have found a solution in new crops and a new brew.
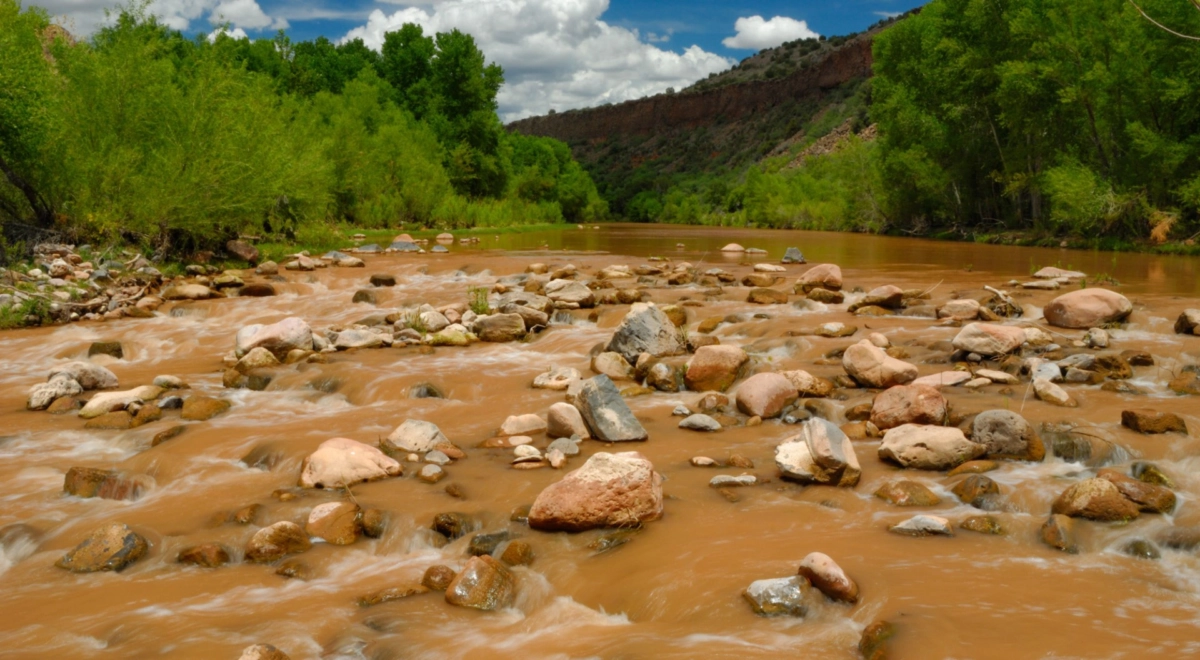

The Verde Riverby Chip Norton
The winding peaks and troughs of Arizona’s Verde Valley, weaving through jagged ochre mountains, dreamy cactus-clad deserts and deep volcanic canyons, make up some of the most iconic images of the American West. For thousands of years, the valley has been home to both the Verde River, one of Arizona’s only perennial wild rivers, and to Indigenous communities from the ancient Sinagua and Hohokam peoples to present-day tribes including the Yavapai, Hopi, Apache and Zuni. It is also home to 270 species of birds, 94 species of mammals and 76 species of native amphibians and reptiles. All this makes the Verde River key to the history, culture and ecosystem of central Arizona.
The human pressures on the river’s resources have come about through a combination of the valley as attractive farmland, significant urban growth and an influx of tourists wanting to hike, boat, bike and bird-watch. The population of Phoenix, which relies on water from a combination of the Verde and Colorado rivers, has grown to 4.75 million in 2024 from 221,000 in 1950, now the fifth largest city in the US, while climate change and agricultural demands have placed additional pressure on the river’s supply.
Global environmental nonprofit The Nature Conservancy has been working on the Verde River for more than 50 years, and as the issue of low water flow became increasingly critical about 15 years ago, it began working with local communities to effect change and save water. This was the launch of Sinagua Malt, Arizona’s first malt house, a Certified B Corp public benefit corporation, which works by incentivizing farmers to transition from water-intensive summer crops such as corn and alfalfa to barley, by providing them with a stable market and offering local breweries and distilleries the opportunity to use locally sourced malt. This measure has saved more than 725 million gallons of Verde River water between 2016 and 2023, according to data from The Nature Conservancy—or more than 50 gallons per pint of beer.
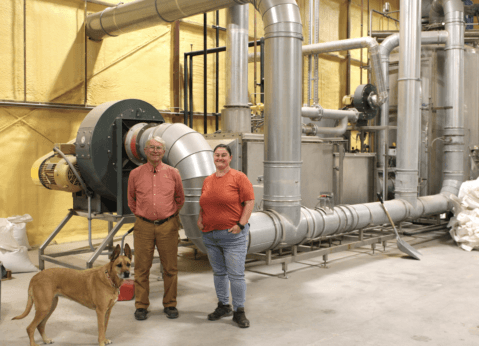
Barley to the rescue
It was a 2015 meeting between The Nature Conservancy’s Kim Schonek and the Verde Conservation District’s Chip Norton that resulted in the game-changing plan to conserve the Verde River flow. The idea for Sinagua Malt came about through Schonek’s and Norton’s shared goals, approached from different perspectives. For Schonek, the key objective was elevating flows in the river, along with protecting farmland and ensuring its viability. Having tried fallowing agreements, where farmers were paid not to farm, and drip irrigation, which was hard for farmers to manage in large areas, they needed a new initiative. “We were also looking for a crop that would still be profitable while using significantly less water in the area—and barley was an obvious choice,” explains Schonek.
Barley is planted in January and February, so it receives a lot of water from the winter rains as it irrigates. It dries out through May and is harvested in June, when the river is at its lowest. Conversely, alfalfa or corn need one foot of water per acre of irrigation during June, which places a significant burden on the river.
Norton came to the issue of water flow through his work on habitat preservation in the Verde. During this time, Schonek and Norton had both built strong relationships with local farmers, and they were able to convince nearby Hauser Farms to take part.
The initial test batch of 15 acres of Harrington two-row malt barley was planted and harvested in 2016, but it had to be sent to Austin for malting, as there were no malting houses in Arizona. When the returning malt was tested by local breweries, including Arizona Wilderness and Sedona Brewing, and found to be of saleable, usable quality, Norton and Schonek were left with a conundrum: The transportation costs and environmental impact of sending their barley all the way to Central Texas negated any savings for local farmers and brewers, as well as some of the benefit to the river. They needed to malt closer to the source, and the only way to do that was to build their own malt house.

Learn by doing
“It worked because Chip didn’t expect anyone else to do stuff—he just jumped in and did it. He was willing to be the guy to make it happen,” says Schonek. Norton came out of retirement to start the business. His background as a project manager in water and wastewater plant construction came in handy. “I had a great deal of experience with automated process equipment in my previous career, but I knew nothing about farming or grain processing,” he says. “My training as a maltster was essentially being thrown in the lake and learning to swim. It has been a steep learning curve.”
After researching technique and recipes through various resources, including the equipment manufacturer and the Craft Maltsters Guild, Norton “just started doing it.” Although Norton says his first batch was “the easiest I’ve ever made,” it wasn’t long before the realities of running a malt house single-handedly set in. “Malting needs cool weather, and there was no air conditioning, which was very challenging in the summer as it was 95 degrees inside—I had to go and buy blocks of ice to throw in the steep water by hand to keep things cool,” he says. There was also a great deal to learn, and batches didn’t always go to plan. Norton says he “learned the correlation between fields that didn’t yield well by quality of barley, so good communication with farmers was crucial. I didn’t have a mentor so I had to self teach—so we learned which fields not to harvest, what techniques gave the best consistency of quality and, over time, we’re making good malt on a small pilot scale.”

Communication is key
Schonek emphasizes the importance of Norton’s persistence but also of strong communication and integrated goals shared between herself and Norton, the farmers and the brewers. “The brewers’ willingness to try malt that maybe wasn’t the greatest was critical,” she says. Sinagua’s stable of three to four breweries kept them at full capacity, until additional investors funded a new malthouse, which has scaled up production to 1,700 tons from 150 tons per year. Sinagua is now operating at a capacity where it is looking for new farms and new breweries and distilleries to work with.
The Nature Conservancy measures the change in the Verde River watershed by evaluating the change in crop and how much water each crop uses. It compares the volume of water used to grow barley to that which alfalfa and corn require per acre to see the savings. Measurements are taken during the summer months when the river is at its lowest ebb, and the pair estimates that its initiative has saved 725 million gallons of water. They’ve been able to grow to 610 acres this year from 95 acres of barley produced in 2016. Sinagua Malt now works with five farms, including Hauser, the Yavapai-Apache Nation’s Cloverleaf Ranch and the Salt River Pima-Maricopa Indian Community’s Hatler Farm. They estimate they will be able to supply upwards of 25 local breweries and distilleries by the end of 2024.
Schonek says there has definitely been more water in the last few years. “You can go boating again now,” she says, “and we expect the impact on the river to at least triple with the new production facility.”
“It’s a dream come true to have such a meaningful impact on the river flow,” says Norton. However, the pair is keen to highlight that there were things they could have done differently along the way and things that have been essential to making the project work.
“Looking back, one more year of assessment before launching would have been beneficial,” says Norton. They both emphasize that you can’t second-guess the future, but that thorough planning, communication and responsibility are essential when working with multiple partners. “It is critical to listen to agricultural partners and understand what their options are—and to have partners who are on board with shared goals and willing to take some level of risk but also help them manage that risk,” says Schonek. The Nature Conservancy initially helped farmers manage the risk by offering compensation for failed batches, although this has now ceased. It also played an integral role in getting investment from donors, a process by which both Norton and Schonek had to present the venture as practical and profitable. The pair emphasizes goal alignment with other complementary initiatives, such as Friends of the Verde River’s Verde River Exchange Water Offset Program, to which Sinagua contributes, and The Nature Conservancy’s work on eliminating waste in water conveyance and ground water management to ensure the best possible outcomes.
When it comes to solving the kind of social and environmental issue that the Verde River flow raised, persistence is the key for Norton. “To achieve results, you have to keep plugging away and not quit—things don’t fall in your lap,” he says. Schonek puts creative problem-solving at the forefront. “We can’t just do what we did last year or what we did a decade ago. We must learn from what we’ve done, scale up and invest in better infrastructure,” she says, highlighting the need for greater funding and policy work across the board.
Follow us
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Want to republish a Modern Farmer story?
We are happy for Modern Farmer stories to be shared, and encourage you to republish our articles for your audience. When doing so, we ask that you follow these guidelines:
Please credit us and our writers
For the author byline, please use “Author Name, Modern Farmer.” At the top of our stories, if on the web, please include this text and link: “This story was originally published by Modern Farmer.”
Please make sure to include a link back to either our home page or the article URL.
At the bottom of the story, please include the following text:
“Modern Farmer is a nonprofit initiative dedicated to raising awareness and catalyzing action at the intersection of food, agriculture, and society. Read more at <link>Modern Farmer</link>.”
Use our widget
We’d like to be able to track our stories, so we ask that if you republish our content, you do so using our widget (located on the left hand side of the article). The HTML code has a built-in tracker that tells us the data and domain where the story was published, as well as view counts.
Check the image requirements
It’s your responsibility to confirm you're licensed to republish images in our articles. Some images, such as those from commercial providers, don't allow their images to be republished without permission or payment. Copyright terms are generally listed in the image caption and attribution. You are welcome to omit our images or substitute with your own. Charts and interactive graphics follow the same rules.
Don’t change too much. Or, ask us first.
Articles must be republished in their entirety. It’s okay to change references to time (“today” to “yesterday”) or location (“Iowa City, IA” to “here”). But please keep everything else the same.
If you feel strongly that a more material edit needs to be made, get in touch with us at [email protected]. We’re happy to discuss it with the original author, but we must have prior approval for changes before publication.
Special cases
Extracts. You may run the first few lines or paragraphs of the article and then say: “Read the full article at Modern Farmer” with a link back to the original article.
Quotes. You may quote authors provided you include a link back to the article URL.
Translations. These require writer approval. To inquire about translation of a Modern Farmer article, contact us at [email protected]
Signed consent / copyright release forms. These are not required, provided you are following these guidelines.
Print. Articles can be republished in print under these same rules, with the exception that you do not need to include the links.
Tag us
When sharing the story on social media, please tag us using the following: - Twitter (@ModFarm) - Facebook (@ModernFarmerMedia) - Instagram (@modfarm)
Use our content respectfully
Modern Farmer is a nonprofit and as such we share our content for free and in good faith in order to reach new audiences. Respectfully,
No selling ads against our stories. It’s okay to put our stories on pages with ads.
Don’t republish our material wholesale, or automatically; you need to select stories to be republished individually.
You have no rights to sell, license, syndicate, or otherwise represent yourself as the authorized owner of our material to any third parties. This means that you cannot actively publish or submit our work for syndication to third party platforms or apps like Apple News or Google News. We understand that publishers cannot fully control when certain third parties automatically summarize or crawl content from publishers’ own sites.
Keep in touch
We want to hear from you if you love Modern Farmer content, have a collaboration idea, or anything else to share. As a nonprofit outlet, we work in service of our community and are always open to comments, feedback, and ideas. Contact us at [email protected].by Ruvani de Silva, Modern Farmer
March 14, 2024
Modern Farmer Weekly
Solutions Hub
Innovations, ideas and inspiration. Actionable solutions for a resilient food system.
ExploreExplore other topics
Share With Us
We want to hear from Modern Farmer readers who have thoughtful commentary, actionable solutions, or helpful ideas to share.
SubmitNecessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly. This category only includes cookies that ensures basic functionalities and security features of the website. These cookies do not store any personal information.
Any cookies that may not be particularly necessary for the website to function and are used specifically to collect user personal data via analytics, ads, other embedded contents are termed as non-necessary cookies.
Has the shift to barley from corn, for example, made a measurable difference in the Verde River’s water flow? I ask because I am thinking that there are likely new demands for water, such as for new residential or business developments, that are reducing river flow.
We see how much water has been saved but how much water does the malt house use? Just curious.
I would very much like to see these two questions answered. Sinagua? Hauser Farms? Nature Conservancy?
It’s a form of leisure not limited to the younger generation but embraced by people of all ages.