The Medieval Origins of Thanksgiving Dinner
Delving into the traditions behind the big feast.
The Medieval Origins of Thanksgiving Dinner
Delving into the traditions behind the big feast.

A portion of the Bayeux Tapestry, c. 1070.courtesy of the Bayeux Museum.
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
How and why did the dishes served at Thanksgiving dinner come to be so fixed?
Many assume that most of them were simply eaten by the Pilgrims during the first Thanksgiving. For this reason, they continue to be eaten today. And it’s true that most of the ingredients are American in origin: the turkey, cranberries, pumpkin, sweet potatoes—even the green beans in the casserole and the pecans in the pie.
Yet we only have one firsthand account of the “first” Thanksgiving—a brief paragraph by Edward Winslow that doesn’t mention any of these foods. And it’s been shown, time and again, that the idea of a unique culinary tradition originating from a feast between the Pilgrims and their Native American neighbors is more advertising myth than historical truth.
But maybe there is something, nonetheless, that’s very traditional about this meal.
In fact, there may be a very good reason these particular dishes—and even the way we eat the meal—came to be strongly associated with Thanksgiving. The first Americans simply mimicked or adapted the traditional fare, flavor combinations and rituals of Europe, using them to fashion the popular dishes we continue to enjoy today.
Alaye that fesande!
To start, think of when we eat the meal: always in the early afternoon, which is just as a proper dinner would have been served 400 years ago. Back then, supper was a smaller, evening meal. Of course, there are other early dinners that families traditionally observe (especially on Sunday). But Thanksgiving always has been, and continues to be, early. It didn’t simply start sooner to accommodate a football game.
As for the ritual of carving at the table, it’s not something we normally do. But it was positively fashionable when the colonists left Europe in the 17th century. There were even carving manuals replete with illustrations for serving their favorite roasts, which were almost always wild fowl. The only difference is that they would hold the entire bird up in the air to carve thin slices, which would fall gently on each diner’s plate. (With today’s huge, domestic turkeys, it’s understandable that we leave them on the platter.)
There was even a whole language of dismemberment in medieval England: you would lyfte that swanne, alaye that fesande, wynge that partyche, dysplaye that crane, but breke that egryt.
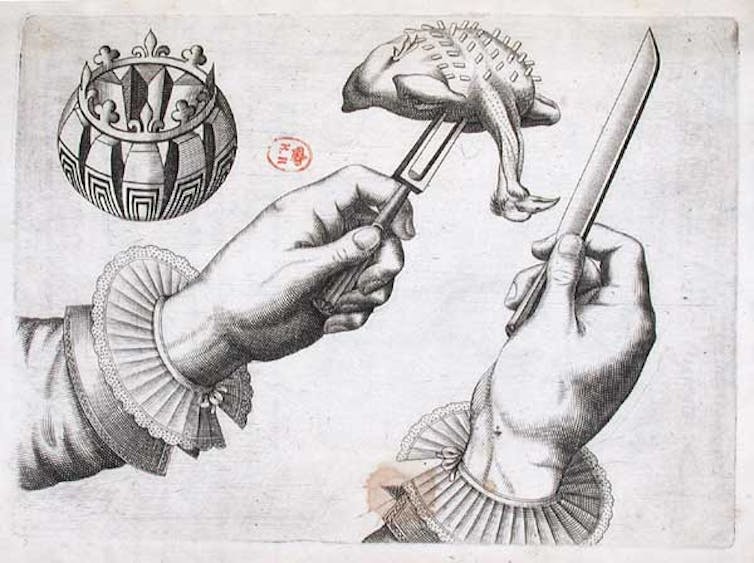
Raspberry sauce and pompion-pye
As for the turkey itself, it was one of the few New World foods that had already gained immediate acceptance in Europe, precisely because of its similarity to peacocks and pheasants, which were among the era’s most fashionable foods. In other words, the Englishmen who landed in Massachusetts didn’t eat turkey because it was the only local food available. Rather, they’d been quite familiar with it back in England, where it was even common to remove the skin and feathers, cook it and serve it with the feathers replaced, as if it were still living—a standard medieval trick.
The side dishes also date back to Europe, with flavor profiles that are actually medieval in origin.
Take cranberry sauce. In medieval Europe, sour fruit sauce with wild fowl was a popular combination, one that balanced a cold and moist condiment with a hot, dry meat. In the mid-17th century, for example, the famous French chef La Varenne served turkey with raspberries.
But the real connection between Thanksgiving and the medieval feast is in the spices. Although today we use the blanket term “pumpkin spice” to characterize variations of cinnamon, nutmeg, clove and ginger (and they show up practically everywhere in cheap artificial form), these flavors were the backbone of medieval cuisine, appearing in a wide array of sweet and savory dishes, from chicken to pasta.
Back then, it simply wasn’t a lavish meal without a riot of spices (which, because they needed to be imported from Asia, were wildly expensive). Today the only one of these spices that stays on the table year-round is pepper. But their pivotal role in Thanksgiving again is a reminder of the tradition’s remote origins.
And many think of green bean casserole as a classic postwar dish—invented in the 1950s as a way to use up all the cans of cream of mushroom soup that had amassed in the pantry. But “French beans” (from America) were already well-known and loved in 17th-century Europe. English Poet Gervase Markham, in 1608’s Farewel to Husbandry, remarks how tender they are when stewed. And Thomas Tryon, a British author of self-help books, writes in The Way to Health, Long Life and Happiness that French beans “far exceed and are much better than other pulses eaten green.”
Candied yams were also a 16th-century staple. In Shakespeare’s The Merry Wives of Windsor, when Sir John Falstaff exclaims that it should rain kissing comfits and hail potatoes, he is actually talking about Virginia sweet potatoes, which had been brought back to Europe in the late 16th century. (These weren’t just candied; they were also considered an aphrodisiac.)
Famed English chef Robert May in the mid-17th-century cookbook The Accomplisht Cook has a great recipe for (sweet) potato pie, which wouldn’t seem too amiss on the Thanksgiving table today (though with cockscombs, testicles and bone marrow would be considered perhaps a bit overgarnished).
As for that very American pumpkin pie? In the 17th century, it was already quite common. One of the earliest female cookbook authors, Hannah Woolley, has a recipe for “pompion-pye” with the same spices we use today. She also includes apples, which, incidentally, are also thoroughly English in a pie.So despite the picture we have of English colonists adapting to strange new ingredients in their new home, most of the recipes – and those we still insist on having at the Thanksgiving table – were already regular favorites.Remember that when you lift high your (very American) turkey leg, like Henry VIII.
Ken Albala is Professor of History at the University of the Pacific in Stockton, California. He has authored or edited 25 books on food including Eating Right in the Renaissance, Food in Early Modern Europe, Cooking in Europe 1250-1650, The Banquet, Beans (winner 2008 IACP Jane Grigson Award), Pancake, Grow Food, Cook Food, Share Food, Nuts: A Global History and most recently Noodle Soup: Recipes, Techniques, Obsession.
Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly. This category only includes cookies that ensures basic functionalities and security features of the website. These cookies do not store any personal information.
Any cookies that may not be particularly necessary for the website to function and are used specifically to collect user personal data via analytics, ads, other embedded contents are termed as non-necessary cookies.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Want to republish a Modern Farmer story?
We are happy for Modern Farmer stories to be shared, and encourage you to republish our articles for your audience. When doing so, we ask that you follow these guidelines:
Please credit us and our writers
For the author byline, please use “Author Name, Modern Farmer.” At the top of our stories, if on the web, please include this text and link: “This story was originally published by Modern Farmer.”
Please make sure to include a link back to either our home page or the article URL.
At the bottom of the story, please include the following text:
“Modern Farmer is a nonprofit initiative dedicated to raising awareness and catalyzing action at the intersection of food, agriculture, and society. Read more at <link>Modern Farmer</link>.”
Use our widget
We’d like to be able to track our stories, so we ask that if you republish our content, you do so using our widget (located on the left hand side of the article). The HTML code has a built-in tracker that tells us the data and domain where the story was published, as well as view counts.
Check the image requirements
It’s your responsibility to confirm you're licensed to republish images in our articles. Some images, such as those from commercial providers, don't allow their images to be republished without permission or payment. Copyright terms are generally listed in the image caption and attribution. You are welcome to omit our images or substitute with your own. Charts and interactive graphics follow the same rules.
Don’t change too much. Or, ask us first.
Articles must be republished in their entirety. It’s okay to change references to time (“today” to “yesterday”) or location (“Iowa City, IA” to “here”). But please keep everything else the same.
If you feel strongly that a more material edit needs to be made, get in touch with us at editor@modfarmer.com. We’re happy to discuss it with the original author, but we must have prior approval for changes before publication.
Special cases
Extracts. You may run the first few lines or paragraphs of the article and then say: “Read the full article at Modern Farmer” with a link back to the original article.
Quotes. You may quote authors provided you include a link back to the article URL.
Translations. These require writer approval. To inquire about translation of a Modern Farmer article, contact us at editor@modfarmer.com
Signed consent / copyright release forms. These are not required, provided you are following these guidelines.
Print. Articles can be republished in print under these same rules, with the exception that you do not need to include the links.
Tag us
When sharing the story on social media, please tag us using the following: - Twitter (@ModFarm) - Facebook (@ModernFarmerMedia) - Instagram (@modfarm)
Use our content respectfully
Modern Farmer is a nonprofit and as such we share our content for free and in good faith in order to reach new audiences. Respectfully,
No selling ads against our stories. It’s okay to put our stories on pages with ads.
Don’t republish our material wholesale, or automatically; you need to select stories to be republished individually.
You have no rights to sell, license, syndicate, or otherwise represent yourself as the authorized owner of our material to any third parties. This means that you cannot actively publish or submit our work for syndication to third party platforms or apps like Apple News or Google News. We understand that publishers cannot fully control when certain third parties automatically summarize or crawl content from publishers’ own sites.
Keep in touch
We want to hear from you if you love Modern Farmer content, have a collaboration idea, or anything else to share. As a nonprofit outlet, we work in service of our community and are always open to comments, feedback, and ideas. Contact us at editor@modfarmer.com.by Ken Albala, Modern Farmer
November 25, 2021