How Climate Change Is Affecting Soil Microbiomes
Often overlooked, diverse microbes are the key to healthy soil. How will a warming planet affect them, and what can farmers do to mitigate some of those changes?
How Climate Change Is Affecting Soil Microbiomes
Often overlooked, diverse microbes are the key to healthy soil. How will a warming planet affect them, and what can farmers do to mitigate some of those changes?
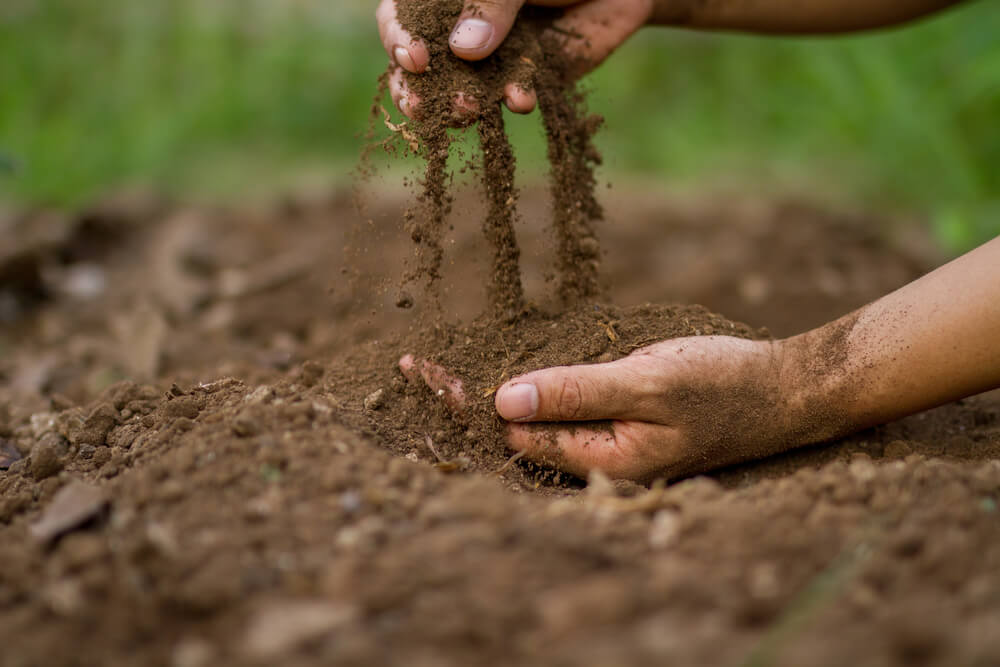

Healthy soil is incredibly complex, made up of with bacteria, protozoa, fungi, actinomycetes, nematodes and others.by Piyaset, Shutterstock.
Most creatures used to illustrate the tragedy of climate change are the familiar variety: Polar bears. Monarch butterflies. Sea turtles. Our soil, however, is often overlooked—it’s teeming with billions of microscopic organisms that comprise the most biodiverse environment on Earth. Like all living things, they’re affected by climate change, too.
There’s a fact that frequently gets mentioned when people talk about soil: There are more microorganisms in a teaspoon of healthy soil than there are people on Earth.
The matrix of living creatures that recycle plant and animal life is incredibly complex, with bacteria, protozoa, fungi, actinomycetes, nematodes and others interacting in countless, largely-unmapped ways. And so, how might drought, excess rainfall, heat and increased CO2 affect those relationships?
Soil microorganisms are the foundation of all life on earth, so it’s a vital question for everyone. If the microbes are out of whack, everything else will be too. But for farmers, it’s particularly crucial. Conventional agriculture, with its chemical inputs and soil degradation, already throws microorganisms and their ecosystems out of balance, with disastrous long-term effects on harvests. Climate change could massively exacerbate the problem.
Exactly what that will look like is unclear. As weather and growing conditions change, could the bacteria and fungi that help plants take up nutrients, for example, shift in their balance with less-beneficial microbes? Could existing pathogens become more powerful? Could there even be a mass die-off?
“Whatever happens, it probably won’t be extreme,” says Jennifer Martiny, a professor of ecology at UC Irvine who focuses on microbial diversity. “Microbes won’t go extinct. They’re very adaptable; they’ll probably survive.”
But beyond that, says Martiny, while it’s certain that microorganisms will be impacted, no one knows exactly how. “The composition of microbes will change with climate change. It will affect functioning,” she says. “But predicting it is pretty hard.”
There are a number of reasons for that uncertainty. The biggest one is the incredible complexity of the soil microbiome and the web of relationships there. Fungi interact with other types of fungi, with bacteria, with the single-celled organisms called protists, with plant roots—and all of it is invisible to the naked eye. Researchers’ efforts to outline that range of connections are still at a very basic stage.
And then there’s the fact that soil microorganisms break down plant organic matter and either store the resulting carbon in the soil or release it into the atmosphere as carbon dioxide. If climate change speeds up their respiration of CO2, it could create a vicious cycle that exacerbates climate effects. The opposite could occur, too, meaning that microbes could dampen the effects of climate change by storing more carbon underground.
Determining what’s likely to happen in the case of increased atmospheric CO2—or other factors like greater heat, and more or less water than usual—has another layer of difficulty: those conditions are hard to mimic in a long-term research context. And the experiments that have been done have largely taken place in naturally-occurring settings like forests and grasslands, not agricultural environments.
Scientists have made some observations about how soil microbes respond under new conditions related to climate change. A colloquium of experts from across the country gathered virtually in November to discuss the topic. A subsequent report determined that climate warming can reduce the diversity of microbes, increase the complexity of their relationships, and speed up their decomposition of soil organic matter. New pathogens are likely to emerge.
The researchers had a caveat, though: these findings might not apply to all soil. After all, the composition of microbes on one farm might be totally different from that of another. “It depends on the soil, always,” says Janet Jansson, chief scientist for biology at the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory and a participant in the colloquium.
But Jansson emphasizes that, across the board, microbes tend to be adaptable. “There’s a funny thing with microorganisms: if you give them a change in environment, resource or condition, they kind of find their way,” she says. “You can have low numbers of some, and given the right conditions, they’ll start to flourish.”
Jennifer Pett-Ridge, a senior staff scientist studying soil microbial ecology at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, agrees. “Each microorganism has a bag of tricks…it’s hard wired to carry out—a defined functional trait space,” she explains. “So here’s one organism that can handle [low oxygen] when it’s flooded, or another that can handle low water potential.” As long as there’s a wide range of microbes in the soil, some of them will thrive under new conditions.
So despite all of the uncertainty about how soil microorganisms will respond to climate change, there actually is an easy answer to growers who might be worried about it: aim for soil populated by a diverse group of microbes.
That might seem difficult to confirm without a microscope, but scientists say it’s actually intuitive. Focus on building healthy soil, and the diversity will come naturally. And healthy soil itself, diverse or not, will confer its own advantages in the face of climate change.
It turns out, conversations over the past decade about soil health and regenerative agriculture are also on the mark when it comes to climate change.
“Soil health is really the basis of a resilient agricultural system. It’s the foundation,” says Matt Wallenstein, former head of the department of soil and crop sciences at Colorado State University, and current chief soil scientist at the agriculture company Syngenta.
Building a resilient agricultural system means cultivating many different plants, because each one offers something different for microbes. Avoiding pesticides is also key, as they can wipe out some of those tiny organisms.

It means disturbing the soil as little as possible too. Among other benefits, farmers who till their land only shallowly or not at all help maintain mycorrhizae, a beneficial fungus that connects plant roots with nutrients and other microbes. Some research has shown that mycorrhizal fungi can help a plant maintain productivity in the face of drought.
Different researchers emphasize different practices. “If I want to keep my microbes happy, what can I do? I think it comes down to soil organic matter—it tends to buffer the system,” says Daniel Buckley, a microbial ecologist at Cornell University. He recommends seasonal use of cover crops. Others say regular applications of compost are key.
Some companies—Syngenta among them—have developed probiotics or bioinoculants that utilize beneficial microbes. While these could potentially be useful to boost natural microbial activity in the face of climate change, research on their effectiveness isn’t decisive.
For now, the best way to prepare for climate change’s effects on microorganisms is to nurture the soil as best as possible. “Microbes are our allies—a friend of the farmer,” says Wallenstein. “As long as we take care of them by good stewardship and management of our soils, they’ll do their part in helping support plant health.”
Follow us
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Want to republish a Modern Farmer story?
We are happy for Modern Farmer stories to be shared, and encourage you to republish our articles for your audience. When doing so, we ask that you follow these guidelines:
Please credit us and our writers
For the author byline, please use “Author Name, Modern Farmer.” At the top of our stories, if on the web, please include this text and link: “This story was originally published by Modern Farmer.”
Please make sure to include a link back to either our home page or the article URL.
At the bottom of the story, please include the following text:
“Modern Farmer is a nonprofit initiative dedicated to raising awareness and catalyzing action at the intersection of food, agriculture, and society. Read more at <link>Modern Farmer</link>.”
Use our widget
We’d like to be able to track our stories, so we ask that if you republish our content, you do so using our widget (located on the left hand side of the article). The HTML code has a built-in tracker that tells us the data and domain where the story was published, as well as view counts.
Check the image requirements
It’s your responsibility to confirm you're licensed to republish images in our articles. Some images, such as those from commercial providers, don't allow their images to be republished without permission or payment. Copyright terms are generally listed in the image caption and attribution. You are welcome to omit our images or substitute with your own. Charts and interactive graphics follow the same rules.
Don’t change too much. Or, ask us first.
Articles must be republished in their entirety. It’s okay to change references to time (“today” to “yesterday”) or location (“Iowa City, IA” to “here”). But please keep everything else the same.
If you feel strongly that a more material edit needs to be made, get in touch with us at [email protected]. We’re happy to discuss it with the original author, but we must have prior approval for changes before publication.
Special cases
Extracts. You may run the first few lines or paragraphs of the article and then say: “Read the full article at Modern Farmer” with a link back to the original article.
Quotes. You may quote authors provided you include a link back to the article URL.
Translations. These require writer approval. To inquire about translation of a Modern Farmer article, contact us at [email protected]
Signed consent / copyright release forms. These are not required, provided you are following these guidelines.
Print. Articles can be republished in print under these same rules, with the exception that you do not need to include the links.
Tag us
When sharing the story on social media, please tag us using the following: - Twitter (@ModFarm) - Facebook (@ModernFarmerMedia) - Instagram (@modfarm)
Use our content respectfully
Modern Farmer is a nonprofit and as such we share our content for free and in good faith in order to reach new audiences. Respectfully,
No selling ads against our stories. It’s okay to put our stories on pages with ads.
Don’t republish our material wholesale, or automatically; you need to select stories to be republished individually.
You have no rights to sell, license, syndicate, or otherwise represent yourself as the authorized owner of our material to any third parties. This means that you cannot actively publish or submit our work for syndication to third party platforms or apps like Apple News or Google News. We understand that publishers cannot fully control when certain third parties automatically summarize or crawl content from publishers’ own sites.
Keep in touch
We want to hear from you if you love Modern Farmer content, have a collaboration idea, or anything else to share. As a nonprofit outlet, we work in service of our community and are always open to comments, feedback, and ideas. Contact us at [email protected].by Amanda Abrams, Modern Farmer
July 11, 2022
Modern Farmer Weekly
Solutions Hub
Innovations, ideas and inspiration. Actionable solutions for a resilient food system.
ExploreExplore other topics
Share With Us
We want to hear from Modern Farmer readers who have thoughtful commentary, actionable solutions, or helpful ideas to share.
SubmitNecessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly. This category only includes cookies that ensures basic functionalities and security features of the website. These cookies do not store any personal information.
Any cookies that may not be particularly necessary for the website to function and are used specifically to collect user personal data via analytics, ads, other embedded contents are termed as non-necessary cookies.
Direct sun should never hit soil. Mulch it and you keep the micro folks happy. When it’s too hot above ground, if the soil is shaded, it will be cooler below ground, and if that mulch rots down to compost that’s even better. Mulch also keeps plant roots cooler. Not many plants set bud beyond 95 degrees, Giant fields and giant machinery are not good for soil. Soil is one of those natural structures that make life on Earth possible. We’re still ruining it or letting it wash away as if it meant nothing. Some ecological literacy might be in… Read more »
The problem with climate change, the unrecognised problem, is that the general population is not responding in a coherent manner to oft repeated and increasingly strident warnings.
And it is not just warnings; even the most striking examples of its impact today; the destruction of the rain forests, the melting of glaciers and ice caps, the bleaching of the great coral reef in Australia, forest fires, droughts, and floods, all these are having little impact on public opinion. But why is this happening ?
One organisation has an answer, check out “Stop Selling the Desert”.
If you are not aware of the SAVE SOIL global mouvement please visit the link below, you will find all the information already.
https://www.consciousplanet.org/
The paragraph about carbon sequestration quotes old science. New science says that photosynthesis in a plant breaks down CO2 into C, which becomes sucrose stored in a plant’s root structure, and O2 that all living things breathe. Photosynthesis does not emit CO2.